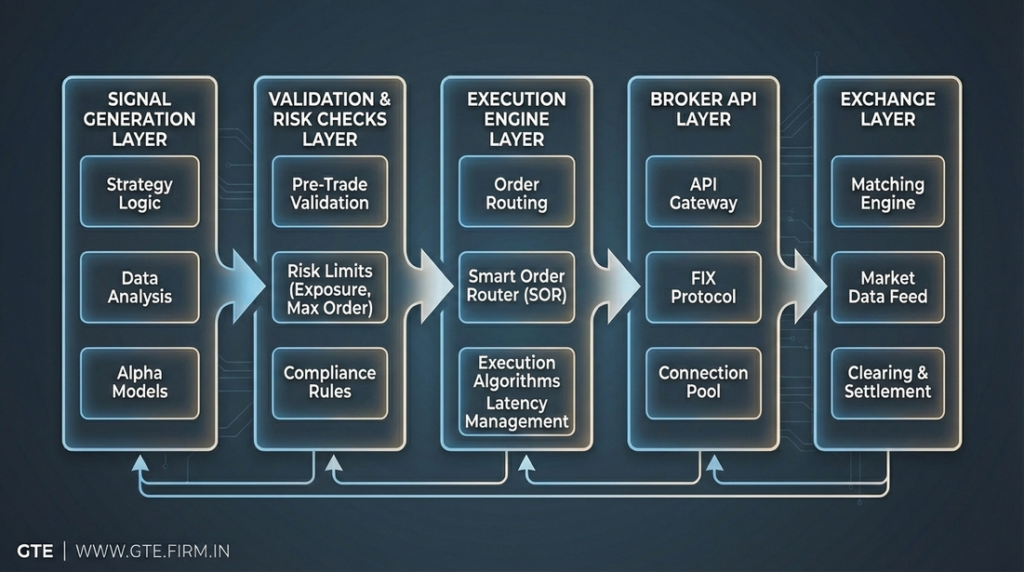
Algorithmic Trading Execution Architecture
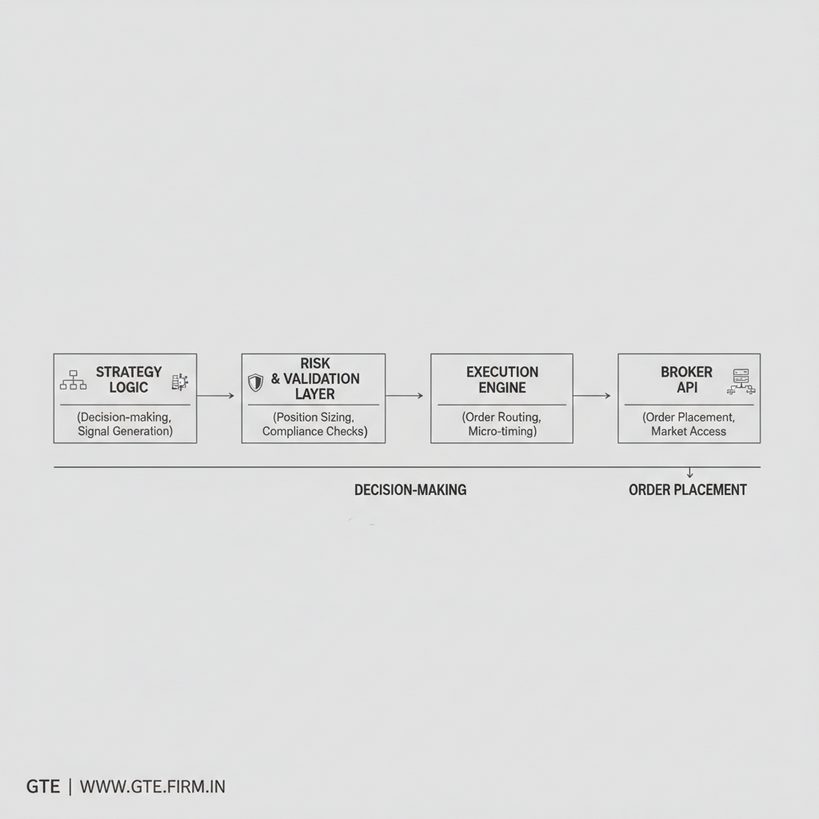
Execution architecture defines how trading decisions are transformed into broker-executed orders.
In algorithmic trading, most failures do not originate from strategy logic. They occur at the execution layer — where signals meet real-world constraints such as broker APIs, latency, order rejections, and market microstructure.
What Execution Architecture Actually Means
Execution architecture refers to the structured system responsible for:
- Receiving trading intent from strategies or signals
- Validating orders against predefined constraints
- Routing orders to brokers or exchanges
- Handling acknowledgements, rejections, and errors
This layer exists independently of market prediction or strategy confidence.
Why Execution Architecture Matters
In live markets, execution quality directly impacts outcomes.
Poorly designed execution systems lead to:
- Unexpected rejections or partial fills
- Duplicate or missed orders
- Uncontrolled exposure during fast markets
- Silent failures without audit trails
Execution architecture exists to ensure that every action is deliberate, validated, and observable.
Core Components of an Execution Architecture
1. Intent Intake
This component receives trade intent from:
- Strategies
- Signals
- Alerts
Intent describes what is desired, not what will be executed.
2. Validation and Risk Enforcement
Before any order reaches a broker, execution systems enforce constraints such as:
- Position limits
- Exposure caps
- Time-based restrictions
- Account and instrument checks
This layer operates even if strategy logic is confident.
3. Execution Engine
The execution engine is responsible for:
- Order formatting
- Retry logic
- Error handling
- Status tracking
It is a technical system, not a decision-maker.
4. Broker API Interface
This component manages communication with brokers.
- Authentication
- Rate limits
- Exchange-specific requirements
Broker APIs are unreliable by design. Execution architecture compensates for this reality.
Why TradingView Should Not Be the Execution Layer
Charting and analysis platforms are not designed to handle:
- Order retries
- Partial fills
- Session state
- Audit logging
Execution logic must live outside analytical platforms to remain controlled and scalable.
Execution Is Infrastructure, Not Strategy
Execution architecture does not predict markets.
It ensures that:
- Every order is intentional
- Failures are contained
- Behaviour is traceable
Well-designed systems treat execution as infrastructure — not as an afterthought.
Where This Page Fits
This page explains how algorithmic trading decisions reach brokers.
For system-wide context, see:
Algorithmic Trading – A Systematic Approach →
For execution risk controls, refer to:
Managing Risks & Alerts in Algorithmic Trading →
Strategies decide. Systems enforce. Execution delivers.